Worksheet on dna rna and protein synthesis answer key – Delve into the intricacies of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis with this comprehensive worksheet and answer key. From the fundamental concepts to the practical applications, this guide unravels the secrets of these vital biological processes, empowering you with a deeper understanding of life’s molecular machinery.
This worksheet provides a structured framework for exploring the key aspects of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis, including their structure, function, and regulation. Engage with interactive exercises and thought-provoking questions that reinforce your understanding and solidify your knowledge.
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis are fundamental processes that underpin the functioning of all living organisms. These processes enable cells to store, transmit, and express genetic information, leading to the production of essential molecules for life.
DNA Structure and Replication: Worksheet On Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis Answer Key

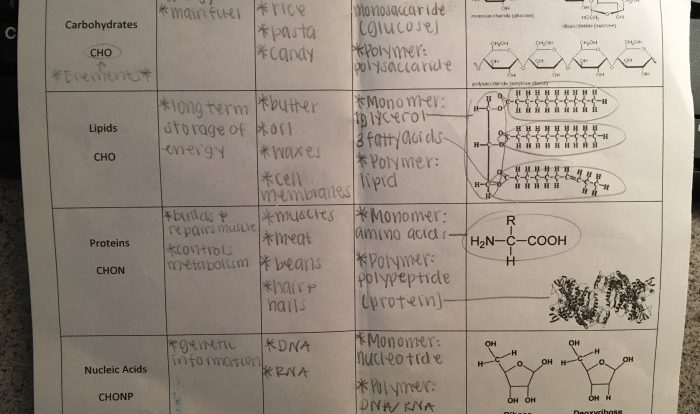
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that stores genetic information in the form of a double helix. It consists of nucleotides, each composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
Base pairing between A and T, and C and G, forms the hydrogen bonds that hold the double helix together.
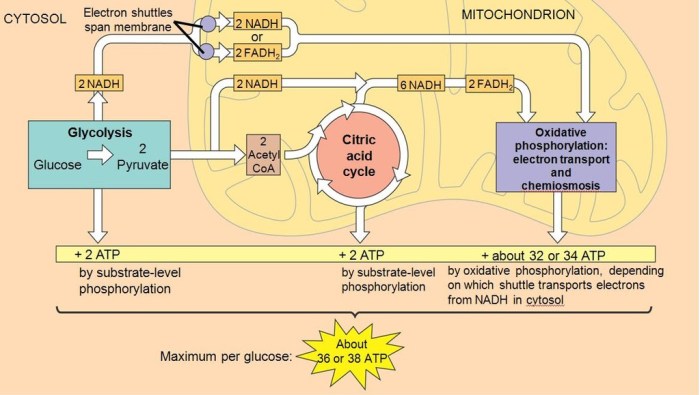
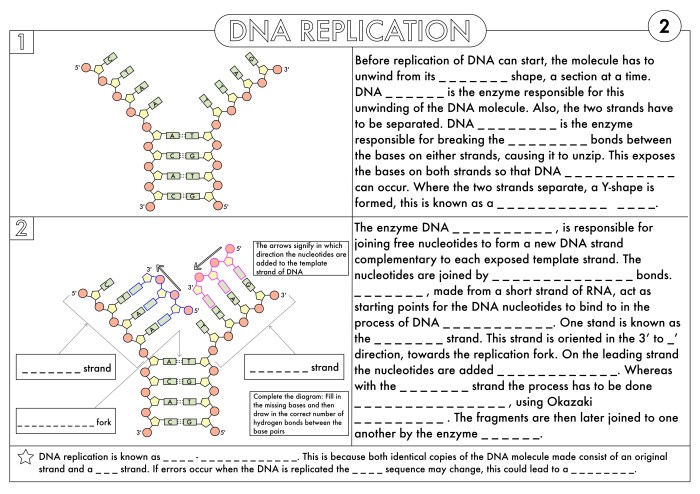
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. During replication, the DNA double helix unwinds, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This semi-conservative process ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which genetic information from DNA is copied into RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA polymerase, an enzyme, binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter and separates the DNA strands. One of the DNA strands serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule, which is then released from the DNA template.
Translation
Translation is the process by which the genetic information in mRNA is converted into a sequence of amino acids to form a protein. Ribosomes, complex molecular machines, bind to mRNA and move along it, reading the sequence of codons (three-nucleotide sequences) and matching them to complementary anticodons on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules.
Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid, which is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
Regulation of Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which the information in DNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. This process is tightly regulated to ensure that the right proteins are produced at the right time and in the right amounts.
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and either promote or repress transcription. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, can also affect gene expression by altering the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors.
Applications of DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
The understanding of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis has revolutionized biotechnology and medicine.
- Genetic engineering:Scientists can modify DNA to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desired traits.
- Personalized medicine:Genetic information can be used to tailor treatments and predict disease risk.
- Diagnostics:DNA and RNA analysis can be used to diagnose diseases, identify genetic mutations, and determine paternity.
Common Errors and Misconceptions
Misconception:DNA is a single molecule that controls all aspects of an organism’s traits.
Truth:DNA is one of many factors that influence traits, along with environmental factors and interactions with other genes.
Misconception:All mutations are harmful.
Truth:Some mutations are neutral or even beneficial, leading to genetic diversity and evolution.
Further Reading and Resources, Worksheet on dna rna and protein synthesis answer key
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. It allows cells to divide and maintain a complete copy of their genetic material, preserving the integrity of the genome.
How does transcription differ from translation?
Transcription involves the synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA as a template. Translation, on the other hand, utilizes mRNA molecules to direct the synthesis of proteins, converting the genetic code into a functional form.
What factors regulate gene expression?
Gene expression is regulated by various mechanisms, including transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and environmental cues. These mechanisms control the production of specific proteins, allowing cells to respond to changing conditions and maintain cellular homeostasis.