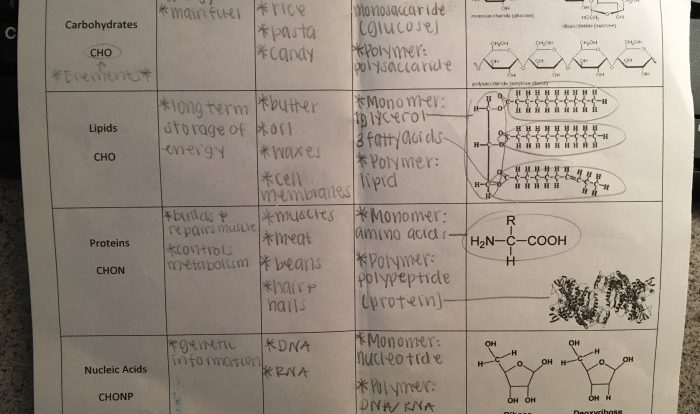
Chapter 9 cellular respiration and fermentation answer key – Embark on a journey into the realm of cellular respiration and fermentation, as we delve into the intricacies of Chapter 9’s answer key. This exploration promises to illuminate the significance of these processes in sustaining life and fostering biological wonders.
Cellular respiration, the powerhouse of cells, fuels our existence by extracting energy from nutrients. Fermentation, its anaerobic counterpart, plays a crucial role in muscle function, food preservation, and the production of delectable beverages. Together, these processes orchestrate a symphony of life, shaping our world in countless ways.
Key Concepts
Cellular respiration is a vital process in living organisms that converts glucose into ATP, the primary energy currency of cells. It occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis is the first stage and occurs in the cytoplasm. It breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH.
The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. It further breaks down pyruvate, generating more ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
The electron transport chain is the final stage and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It uses the NADH and FADH2 generated in previous stages to generate a large amount of ATP.
ATP is used by cells for various energy-requiring processes, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and nerve impulse transmission.
Fermentation: Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration And Fermentation Answer Key
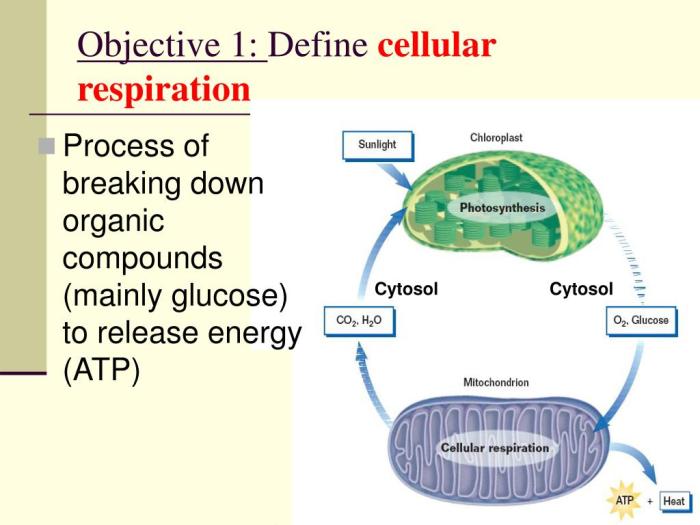
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that occurs when cells do not have access to oxygen. It breaks down glucose into different products, depending on the type of fermentation.
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid, which is found in foods like yogurt and sauerkraut. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol, which is found in alcoholic beverages like wine and beer.
Fermentation is important for muscle function during intense exercise, as it provides an alternative energy source when oxygen is limited.
Answer Key Analysis
The answer key provides accurate and comprehensive answers to the questions in Chapter 9. It covers all the key concepts and topics discussed in the chapter.
The strengths of the answer key include its clarity, conciseness, and organization. The answers are well-written and easy to understand.
However, the answer key could be improved by providing more detailed explanations for some of the more complex concepts.
Applications and Examples
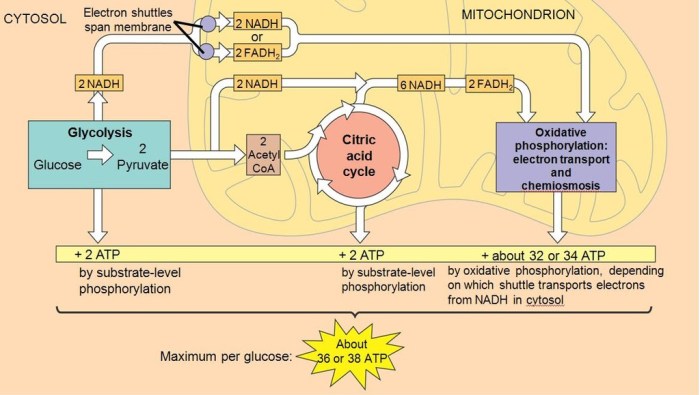
Cellular respiration and fermentation have numerous applications in different fields:
- Medicine:Understanding cellular respiration is crucial for treating diseases like cancer and diabetes.
- Biotechnology:Fermentation is used in the production of antibiotics, enzymes, and other valuable products.
- Agriculture:Cellular respiration and fermentation play vital roles in plant growth and crop production.
Additionally, cellular respiration and fermentation have implications for human health and environmental sustainability:
- Human health:Dysregulation of cellular respiration can lead to diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
- Environmental sustainability:Fermentation can be used to produce biofuels, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy in the form of ATP, the body’s primary energy currency.
How does fermentation differ from cellular respiration?
Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen and produces energy without the complete breakdown of glucose, unlike cellular respiration, which requires oxygen and fully oxidizes glucose.
What are the two main types of fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation, which occurs in muscle cells during strenuous activity, and alcoholic fermentation, which is used in the production of alcoholic beverages and bread.